pentapy Quickstart

pentapy is a toolbox to deal with pentadiagonal matrices in Python and solve the corresponding linear equation systems.
Installation
The package can be installed via pip. On Windows you can install WinPython to get Python and pip running.
pip install pentapy
There are pre-built wheels for Linux, MacOS and Windows for most Python versions.
To get the scipy solvers running, you have to install scipy or you can use the extra argument:
pip install pentapy[all]
Instead of “all” you can also typ “scipy” or “umfpack”.
References
The solver is based on the algorithms PTRANS-I and PTRANS-II
presented by Askar et al. 2015.
Examples
Solving a pentadiagonal linear equation system
This is an example of how to solve a LES with a pentadiagonal matrix.
import numpy as np
import pentapy as pp
size = 1000
# create a flattened pentadiagonal matrix
M_flat = (np.random.random((5, size)) - 0.5) * 1e-5
V = np.random.random(size) * 1e5
# solve the LES with M_flat as row-wise flattened matrix
X = pp.solve(M_flat, V, is_flat=True)
# create the corresponding matrix for checking
M = pp.create_full(M_flat, col_wise=False)
# calculate the error
print(np.max(np.abs(np.dot(M, X) - V)))
This should give something like:
4.257890395820141e-08
Performance
In the following, a couple of solvers for pentadiagonal systems are compared:
Solver 1: Standard linear algebra solver of Numpy
np.linalg.solve(link)Solver 2:
scipy.sparse.linalg.spsolve(link)Solver 3: Scipy banded solver [
scipy.linalg.solve_banded](scipy.github.io/devdocs/generated/scipy.linalg.solve_banded.html)Solver 4: pentapy.solve with
solver=1Solver 5: pentapy.solve with
solver=2
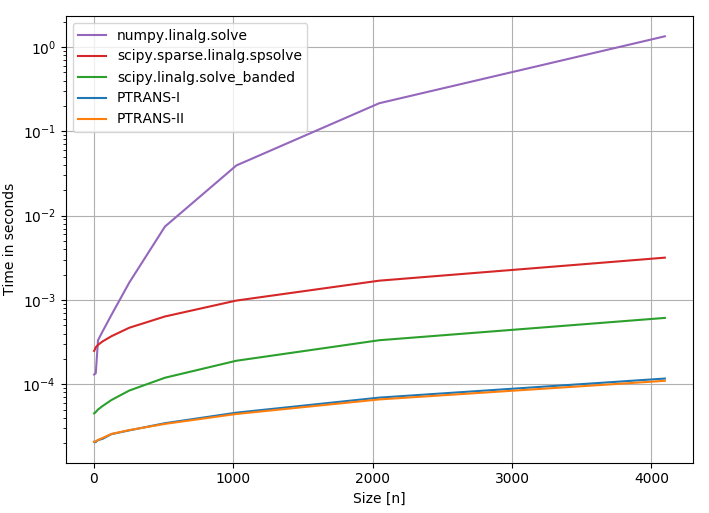
The performance plot was created with perfplot (link).