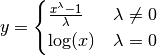gstools.normalizer.BoxCox¶
- class gstools.normalizer.BoxCox(data=None, **parameter)[source]¶
Bases:
gstools.normalizer.base.NormalizerBox-Cox (1964) transformed fields.
- Parameters
data (array_like, optional) – Input data to fit the transformation in order to gain normality. The default is None.
lmbda (
float, optional) – Shape parameter. Default: 1
References
- Box1964
G.E.P. Box and D.R. Cox, “An Analysis of Transformations”, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society B, 26, 211-252, (1964)
- Attributes
denormalize_rangetuple: Valid range for output data depending on lmbda.namestr: The name of the normalizer class.
Methods
denormalize(data)Transform to input distribution.
derivative(data)Factor for normal PDF to gain target PDF.
fit(data[, skip])Fitting the transformation to data by maximizing Log-Likelihood.
kernel_loglikelihood(data)Kernel Log-Likelihood for given data with current parameters.
likelihood(data)Likelihood for given data with current parameters.
loglikelihood(data)Log-Likelihood for given data with current parameters.
normalize(data)Transform to normal distribution.
- denormalize(data)¶
Transform to input distribution.
- Parameters
data (array_like) – Input data (normal distributed).
- Returns
Denormalized data.
- Return type
- derivative(data)¶
Factor for normal PDF to gain target PDF.
- Parameters
data (array_like) – Input data (not normal distributed).
- Returns
Derivative of the normalization transformation function.
- Return type
- fit(data, skip=None, **kwargs)¶
Fitting the transformation to data by maximizing Log-Likelihood.
- Parameters
data (array_like) – Input data to fit the transformation to in order to gain normality.
skip (
listofstrorNone, optional) – Names of parameters to be skiped in fitting. The default is None.**kwargs – Keyword arguments passed to
scipy.optimize.minimize_scalarwhen only one parameter present orscipy.optimize.minimize.
- Returns
Optimal paramters given by names.
- Return type
- kernel_loglikelihood(data)¶
Kernel Log-Likelihood for given data with current parameters.
- Parameters
data (array_like) – Input data to fit the transformation to in order to gain normality.
- Returns
Kernel Log-Likelihood of the given data.
- Return type
Notes
This loglikelihood function is neglecting additive constants, that are not needed for optimization.
- likelihood(data)¶
Likelihood for given data with current parameters.
- Parameters
data (array_like) – Input data to fit the transformation to in order to gain normality.
- Returns
Likelihood of the given data.
- Return type
- loglikelihood(data)¶
Log-Likelihood for given data with current parameters.
- Parameters
data (array_like) – Input data to fit the transformation to in order to gain normality.
- Returns
Log-Likelihood of the given data.
- Return type
- normalize(data)¶
Transform to normal distribution.
- Parameters
data (array_like) – Input data (not normal distributed).
- Returns
Normalized data.
- Return type
- property denormalize_range¶
Valid range for output data depending on lmbda.
(-1/lmbda, inf) or (-inf, -1/lmbda)
- Type