Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
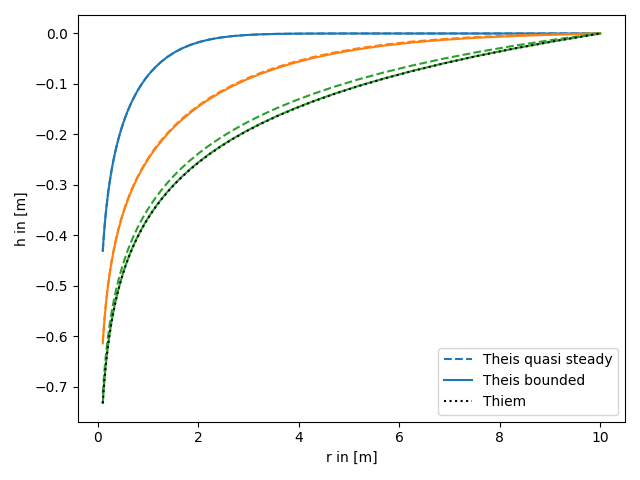
Quasi steady convergence
The quasi steady is reached, when the radial shape of the drawdown in not changing anymore.
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from anaflow import theis, thiem
time = [10, 100, 1000]
rad = np.geomspace(0.1, 10)
r_ref = 10.0
head_ref = theis(
time,
np.full_like(rad, r_ref),
storage=1e-3,
transmissivity=1e-4,
rate=-1e-4,
)
head1 = (
theis(time, rad, storage=1e-3, transmissivity=1e-4, rate=-1e-4) - head_ref
)
head2 = theis(
time, rad, storage=1e-3, transmissivity=1e-4, rate=-1e-4, r_bound=r_ref
)
head3 = thiem(rad, r_ref, transmissivity=1e-4, rate=-1e-4)
for i, step in enumerate(time):
label_1 = "Theis quasi steady" if i == 0 else None
label_2 = "Theis bounded" if i == 0 else None
plt.plot(rad, head1[i], label=label_1, color="C" + str(i), linestyle="--")
plt.plot(rad, head2[i], label=label_2, color="C" + str(i))
plt.plot(rad, head3, label="Thiem", color="k", linestyle=":")
plt.xlabel("r in [m]")
plt.ylabel("h in [m]")
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.185 seconds)