Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Self defined radial conductivity or transmissivity
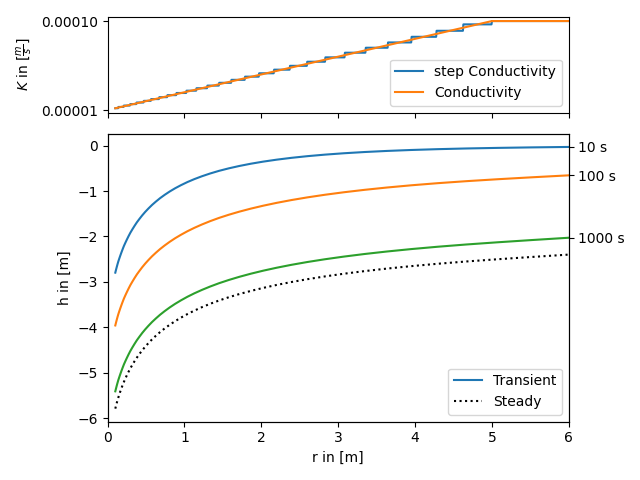
All heterogeneous solutions of AnaFlow are derived by calculating an equivalent step function of a radial symmetric transmissivity resp. conductivity function.
The following code shows how to apply this workflow to a self defined transmissivity function. The function in use represents a linear transition from a local to a far field value of transmissivity within a given range.
The step function is calculated as the harmonic mean within given bounds, since the groundwater flow under a pumping condition is perpendicular to the different annular regions of transmissivity.
Reference: (not yet published)
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from anaflow import ext_grf, ext_grf_steady
from anaflow.tools import annular_hmean, specialrange_cut, step_f
def cond(rad, K_far, K_well, len_scale):
"""Conductivity with linear increase from K_well to K_far."""
return np.minimum(np.abs(rad) / len_scale, 1.0) * (K_far - K_well) + K_well
time_labels = ["10 s", "100 s", "1000 s"]
time = [10, 100, 1000]
rad = np.geomspace(0.1, 6)
K_well = 1e-5
K_far = 1e-4
len_scale = 5.0
dim = 1.5
rate = -1e-4
S = 1e-4
cut_off = len_scale
parts = 30
r_well = 0.0
r_bound = 50.0
# calculate a disk-distribution of "trans" by calculating harmonic means
R_part = specialrange_cut(r_well, r_bound, parts, cut_off)
K_part = annular_hmean(
cond, R_part, ann_dim=dim, K_far=K_far, K_well=K_well, len_scale=len_scale
)
S_part = np.full_like(K_part, S)
# calculate transient and steady heads
head1 = ext_grf(time, rad, S_part, K_part, R_part, dim=dim, rate=rate)
head2 = ext_grf_steady(
rad,
r_bound,
cond,
dim=dim,
rate=-1e-4,
K_far=K_far,
K_well=K_well,
len_scale=len_scale,
)
# plotting
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(2, 1, height_ratios=[1, 3])
ax1 = plt.subplot(gs[0])
ax2 = plt.subplot(gs[1], sharex=ax1)
time_ticks = []
for i, step in enumerate(time):
label = "Transient" if i == 0 else None
ax2.plot(rad, head1[i], label=label, color="C" + str(i))
time_ticks.append(head1[i][-1])
ax2.plot(rad, head2, label="Steady", color="k", linestyle=":")
rad_lin = np.linspace(rad[0], rad[-1], 1000)
ax1.plot(rad_lin, step_f(rad_lin, R_part, K_part), label="step Conductivity")
ax1.plot(
rad_lin, cond(rad_lin, K_far, K_well, len_scale), label="Conductivity"
)
ax1.set_yticks([K_well, K_far])
ax1.set_ylabel(r"$K$ in $[\frac{m}{s}]$")
plt.setp(ax1.get_xticklabels(), visible=False)
ax1.legend()
ax2.set_xlabel("r in [m]")
ax2.set_ylabel("h in [m]")
ax2.legend()
ax2.set_xlim([0, rad[-1]])
ax3 = ax2.twinx()
ax3.set_yticks(time_ticks)
ax3.set_yticklabels(time_labels)
ax3.set_ylim(ax2.get_ylim())
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.399 seconds)