Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Truncated Power Law Variograms
GSTools also implements truncated power law variograms, which can be represented as a superposition of scale dependant modes in form of standard variograms, which are truncated by a lower- \(\ell_{\mathrm{low}}\) and an upper length-scale \(\ell_{\mathrm{up}}\).
This example shows the truncated power law (TPLStable) based on the
Stable covariance model and is given by
\[\gamma_{\ell_{\mathrm{low}},\ell_{\mathrm{up}}}(r) =
\intop_{\ell_{\mathrm{low}}}^{\ell_{\mathrm{up}}}
\gamma(r,\lambda) \frac{\rm d \lambda}{\lambda}\]
with Stable modes on each scale:
\[\begin{split}\gamma(r,\lambda) &=
\sigma^2(\lambda)\cdot\left(1-
\exp\left[- \left(\frac{r}{\lambda}\right)^{\alpha}\right]
\right)\\
\sigma^2(\lambda) &= C\cdot\lambda^{2H}\end{split}\]
which gives Gaussian modes for alpha=2
or Exponential modes for alpha=1.
For \(\ell_{\mathrm{low}}=0\) this results in:
\[\begin{split}\gamma_{\ell_{\mathrm{up}}}(r) &=
\sigma^2_{\ell_{\mathrm{up}}}\cdot\left(1-
\frac{2H}{\alpha} \cdot
E_{1+\frac{2H}{\alpha}}
\left[\left(\frac{r}{\ell_{\mathrm{up}}}\right)^{\alpha}\right]
\right) \\
\sigma^2_{\ell_{\mathrm{up}}} &=
C\cdot\frac{\ell_{\mathrm{up}}^{2H}}{2H}\end{split}\]
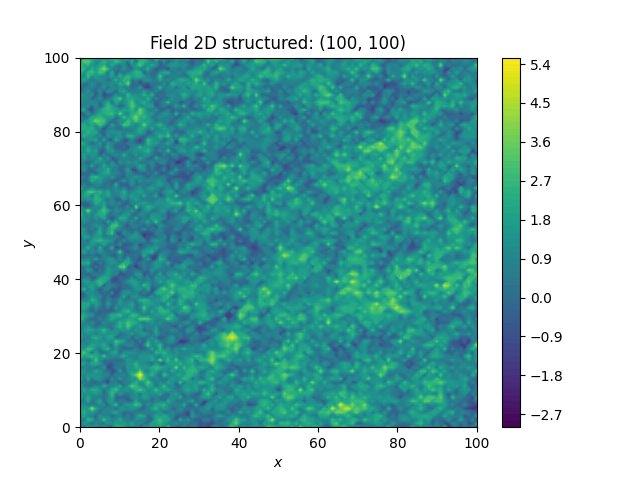
import numpy as np
import gstools as gs
x = y = np.linspace(0, 100, 100)
model = gs.TPLStable(
dim=2, # spatial dimension
var=1, # variance (C is calculated internally, so variance is actually 1)
len_low=0, # lower truncation of the power law
len_scale=10, # length scale (a.k.a. range), len_up = len_low + len_scale
nugget=0.1, # nugget
anis=0.5, # anisotropy between main direction and transversal ones
angles=np.pi / 4, # rotation angles
alpha=1.5, # shape parameter from the stable model
hurst=0.7, # hurst coefficient from the power law
)
srf = gs.SRF(model, mean=1.0, seed=19970221)
srf.structured([x, y])
srf.plot()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 16.653 seconds)