Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Basic Methods
The covariance model class CovModel of GSTools provides a set of handy
methods.
One of the following functions defines the main characterization of the variogram:
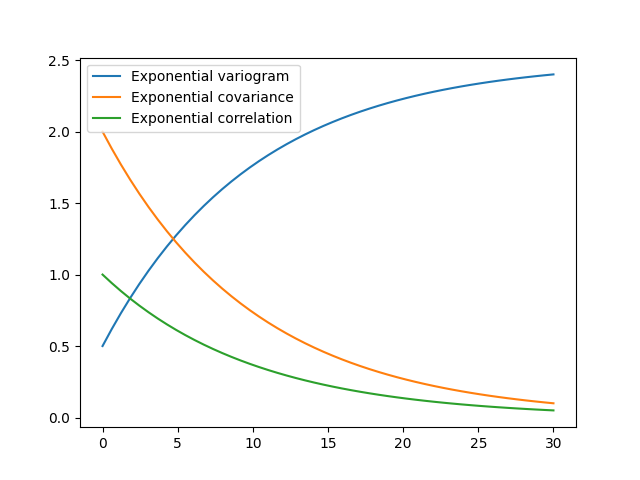
CovModel.variogram: The variogram of the model given by\[\gamma\left(r\right)= \sigma^2\cdot\left(1-\rho\left(r\right)\right)+n\]CovModel.covariance: The (auto-)covariance of the model given by\[C\left(r\right)= \sigma^2\cdot\rho\left(r\right)\]CovModel.correlation: The (auto-)correlation (or normalized covariance) of the model given by\[\rho\left(r\right)\]CovModel.cor: The normalized correlation taking a normalized range given by:\[\mathrm{cor}\left(\frac{r}{\ell}\right) = \rho\left(r\right)\]
As you can see, it is the easiest way to define a covariance model by giving a correlation function as demonstrated in the introductory example. If one of the above functions is given, the others will be determined:
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.151 seconds)